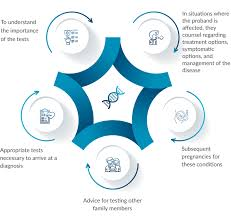
Q. What is the meaning of genetic counseling?
Genetic
counseling is a vital part of modern healthcare that plays a crucial role in
providing individuals and families with the knowledge and understanding they
need to make informed decisions about their health, particularly in relation to
genetic conditions. It involves the process of evaluating genetic risks,
providing information about inherited diseases or conditions, and helping
individuals understand the emotional and social implications of their genetic
predispositions. The importance of genetic counseling lies not only in its
ability to identify genetic disorders but also in the empowerment it offers to
individuals to make proactive health choices, manage risks, and prepare for
potential future health challenges.
At
its core, genetic counseling is a communication process that involves the
interaction between a trained genetic counselor, a physician, and the
individual or family seeking advice. The aim is to provide an accurate
assessment of genetic risks, offer education about genetics, and support decision-making
about testing, prevention, and management options. Genetic counseling can cover
a wide range of topics, including inheritance patterns of specific genetic
conditions, the potential for passing on inherited traits, the likelihood of
developing a hereditary condition, and how to manage or treat those conditions
if they arise.
The
significance of genetic counseling becomes particularly apparent when
considering the role of genetics in the development of many diseases and
conditions. While some diseases are caused solely by environmental factors,
others have a genetic component, which means they can be inherited from one
generation to the next. Inherited conditions can be passed down through various
inheritance patterns, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or
X-linked inheritance. In these cases, the genetic counselor helps families
understand how genetic conditions are passed on and what that means for their
health and the health of their children or future generations.
The
need for genetic counseling is especially important when considering conditions
that are rare but severe or those that have no known cure. In many cases,
individuals with genetic conditions may not exhibit symptoms until later in
life, or the symptoms may be subtle, making early diagnosis and intervention
challenging. Genetic counseling helps identify at-risk individuals or families
and provides them with information about early screening, prevention
strategies, and the latest advancements in treatment options. For instance,
genetic counseling can be essential in cases of inherited cancers like breast
cancer, colon cancer, or ovarian cancer, where specific gene mutations (such as
BRCA1 and BRCA2) increase the risk of developing cancer. By identifying
individuals with these mutations, genetic counselors can guide them in taking
preventive measures like regular screenings or prophylactic surgeries.
Furthermore,
genetic counseling is significant in the context of prenatal and preconception
care. Many couples seek genetic counseling when planning a family, particularly
if they have a known family history of genetic conditions. Through genetic
testing, genetic counselors can assess the risk of passing on inherited
disorders to the offspring. This is particularly valuable for parents who may
be carriers of genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or
Tay-Sachs disease. Counseling sessions can provide couples with information
about the probability of having a child with a genetic condition, as well as
available reproductive options, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) with
genetic screening, preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), or prenatal testing
such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
In
addition to its role in reproductive health, genetic counseling is increasingly
important in the management of chronic diseases with genetic components. For
example, conditions such as Huntington's disease, muscular dystrophy, or cystic
fibrosis are all genetic disorders that require ongoing management and care.
Genetic counselors can help individuals with these conditions and their
families understand the course of the disease, potential complications, and
available treatment options. For families affected by such conditions, genetic
counseling provides essential emotional and psychological support, helping them
cope with the knowledge of a genetic diagnosis and plan for the future.
Beyond
the medical and clinical aspects, genetic counseling also addresses the
ethical, legal, and social implications of genetic testing and genetic
information. As genetic testing becomes more accessible and advanced, ethical
concerns about privacy, discrimination, and informed consent are at the
forefront of genetic counseling discussions. For instance, there is the potential
for genetic information to be misused by insurance companies or employers,
leading to genetic discrimination. In many countries, laws such as the Genetic
Information Non-Discrimination Act (GINA) in the United States have been
enacted to prevent such discrimination, but genetic counselors must still
educate individuals about their rights and the potential risks associated with
genetic testing.
Genetic
counseling also helps individuals understand the psychological impact of
learning about their genetic risks. For some people, receiving information
about a potential genetic condition can be overwhelming, leading to anxiety,
fear, or even guilt. The role of the genetic counselor is to provide emotional
support and offer resources to help individuals process their feelings and make
decisions that are best for their well-being. In cases where a person may be at
risk for a late-onset condition, like Huntington’s disease, genetic counseling
can provide ongoing support as individuals face the uncertainty of whether they
will develop symptoms in the future.
The
field of genetic counseling is continuously evolving as our understanding of
genetics and genomics expands. The advent of whole-genome sequencing and other
advanced genomic technologies has revolutionized the field, allowing genetic
counselors to provide more comprehensive and accurate assessments of genetic
risk. Whole-genome sequencing, for example, can identify rare genetic
variations that may not be detectable through traditional genetic testing. This
has opened new doors for diagnosing previously undiagnosed conditions,
providing individuals with answers and enabling them to make informed decisions
about their health.
Moreover,
the integration of personalized medicine into healthcare has further
highlighted the importance of genetic counseling. Personalized medicine
involves tailoring medical treatment to an individual's genetic makeup,
ensuring that interventions are more effective and have fewer side effects.
Genetic counselors are essential in helping individuals understand how their
genetic profile may influence their response to different treatments, such as
pharmacogenomics, which studies how genetic variations affect drug metabolism.
The
significance of genetic counseling is not limited to individuals with known
genetic conditions or those planning for a family. It is also vital in the
context of rare diseases, where genetic testing may help identify the
underlying cause of symptoms that cannot be explained by conventional
diagnostic methods. In some cases, genetic testing can provide a definitive
diagnosis for individuals with undiagnosed conditions, enabling them to access
appropriate treatments or clinical trials that might otherwise be unavailable.
Genetic
counselors work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics,
research institutions, and public health organizations. In each of these
settings, they collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as
physicians, geneticists, nurses, and social workers, to provide comprehensive
care to patients. Genetic counselors may also be involved in public health
initiatives, where they help raise awareness about genetic conditions and
promote access to genetic testing and counseling services. This is particularly
important in underserved communities, where access to genetic counseling
services may be limited, and where education about genetics and genetic risks
can improve health outcomes.
In
summary, genetic counseling is an essential service that provides individuals
and families with the information, support, and resources they need to navigate
the complexities of genetic health. Whether for understanding inherited
diseases, making informed decisions about reproductive health, managing chronic
conditions, or addressing ethical concerns related to genetic testing, genetic
counseling plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare. Its significance will
only continue to grow as genetic technologies advance and our understanding of
genomics deepens, ultimately empowering individuals to take charge of their
health and make decisions that improve their quality of life.







0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.