Q. Autocratic Style and Demographic Style
Autocratic
Style and Democratic Style of Leadership
Leadership styles
are a key component of leadership theory and practice, shaping how leaders
interact with their followers, make decisions, and manage organizations. Among
the most prominent leadership styles, the autocratic
style and the democratic style
stand out due to their contrasting approaches to decision-making, team
involvement, and communication. These leadership styles have been widely
studied in both organizational theory and practice, as they have a significant
impact on employee satisfaction, productivity, and the overall success of an
organization. This exploration will provide an in-depth analysis of the
autocratic and democratic leadership styles, discussing their characteristics,
advantages, disadvantages, and implications in various organizational contexts.
By comparing and contrasting these styles, we aim to gain a clearer
understanding of their influence on leadership effectiveness and organizational
outcomes.
Autocratic Leadership Style
The autocratic leadership style is one in
which the leader makes decisions unilaterally, without seeking input or
feedback from their subordinates. In this style, the leader has complete
control over all decision-making processes, sets clear guidelines and
expectations, and expects compliance from their team members. Autocratic
leaders tend to centralize authority and prefer to maintain strict supervision
over their employees. This leadership style is also known as authoritarian
leadership, as it places power and control firmly in the hands of the leader.
Autocratic leadership is often seen as effective in situations that require
quick decisions, tight control, or strong direction, but it can also have
negative implications for employee morale and creativity.
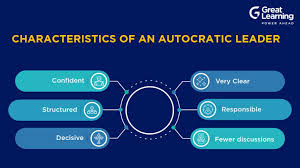
Key
Characteristics of Autocratic Leadership
1.
Centralized
Decision-Making: One of the
defining features of autocratic leadership is that the leader retains the
authority to make decisions without consulting others. This means that the
leader is the sole decision-maker, and employees are expected to follow orders
without question.
2. Clear Expectations
and Structure: Autocratic
leaders typically provide clear instructions to their subordinates and
establish well-defined roles and expectations. This structure can help
employees understand their responsibilities and minimize confusion.
3. Control and
Supervision: Autocratic leaders
tend to closely monitor their team’s performance and closely oversee the work
being done. They may use rewards and punishments to maintain control and ensure
that tasks are completed according to their specifications.
4. Limited Employee Participation: In an autocratic leadership style, employees have
little to no opportunity to participate in decision-making or provide input
into organizational strategies. The leader may not seek feedback from
subordinates or allow them to contribute ideas.
5. Authoritarian
Approach: The autocratic leader
often adopts an authoritarian approach, using power to assert their authority
and ensure compliance. There is typically little room for negotiation or
discussion in this style.
Advantages
of Autocratic Leadership
1.
Quick
Decision-Making: One of the key
advantages of autocratic leadership is the ability to make quick decisions. In
fast-paced environments, where time is of the essence and the need for
immediate action is critical, autocratic leaders can make decisions without
waiting for consensus or input from others.
2. Clear Direction
and Control: Autocratic
leadership provides clear direction, which can be beneficial in situations
where tasks need to be completed precisely and efficiently. Employees
understand exactly what is expected of them and can focus on carrying out tasks
without ambiguity.
3. Effective in
Crisis Situations: In times of
crisis, when rapid responses are needed, the autocratic leadership style can be
highly effective. The leader's ability to make fast, authoritative decisions
can help to minimize chaos and maintain order in urgent situations.
4. Reduced Risk of
Conflict: With the leader
holding all the decision-making power, there is less opportunity for
disagreement or conflict among employees about the direction of the
organization. This can create a more streamlined, cohesive environment where
everyone follows the leader's instructions without hesitation.
5. Accountability: With one person in charge of decision-making,
accountability is clear. If something goes wrong, it is easy to identify the
leader as the person responsible, which can simplify performance evaluation.
Disadvantages
of Autocratic Leadership
1. Lack of Employee
Motivation and Engagement:
Because employees have little say in decision-making, they may feel
disconnected from their work and less motivated to perform at their best. This
lack of empowerment can lead to lower levels of job satisfaction and
engagement.
2. Reduced Creativity
and Innovation: Autocratic
leaders typically do not encourage employees to contribute ideas or challenge
existing processes. As a result, innovation may be stifled, and employees may
not feel inclined to think creatively or suggest improvements.
3. High Turnover Rates: Employees who are dissatisfied with the lack of
autonomy and involvement in decision-making may become frustrated and
eventually leave the organization. High turnover can lead to additional
recruitment and training costs, as well as loss of institutional knowledge.
4. Over-Reliance on
the Leader: Autocratic
leadership can create a situation in which employees rely too heavily on the
leader for direction and guidance. This can lead to a lack of independence and
initiative among team members, limiting their ability to work autonomously.
5. Poor Relationship
Building: The lack of open
communication and collaboration in autocratic leadership can damage
relationships between leaders and employees. The hierarchical nature of this
leadership style can create feelings of resentment or distrust among
subordinates.
When is
Autocratic Leadership Effective?
The autocratic leadership style can be effective in
certain situations, particularly when decisions need to be made quickly and
decisively. For example, in high-pressure industries such as emergency
services, military settings, or manufacturing environments, where efficiency
and strict adherence to protocols are critical, an autocratic approach may be
ideal. Additionally, when managing teams of individuals who require a high
level of structure and direction, autocratic leadership can help ensure that
tasks are completed on time and to a high standard.
However, for organizations that prioritize employee
development, creativity, and engagement, autocratic leadership may not be the
best approach. It is essential for leaders to assess the needs of their team
and the context of their work to determine whether an autocratic style is
appropriate.
Democratic Leadership Style
The democratic leadership style, also known
as participative leadership, is characterized by a more collaborative and
inclusive approach to decision-making. In this style, the leader actively seeks
input and feedback from their subordinates and involves them in the
decision-making process. Democratic leaders foster a sense of shared
responsibility and encourage employees to contribute their ideas, suggestions,
and opinions. The leader ultimately makes the final decision, but the team’s
input is highly valued and often incorporated into the decision-making process.
This leadership style is often associated with higher levels of employee
satisfaction, engagement, and creativity, as it provides a more supportive and
empowering environment for team members.
Key
Characteristics of Democratic Leadership
1.
Shared
Decision-Making: Democratic
leaders involve their team members in the decision-making process. While the
leader may retain the final say, they encourage input and value the
perspectives of their subordinates. This fosters a sense of ownership and
engagement among employees.
2. Open Communication: Democratic leaders promote open communication within
the team. They encourage feedback, active listening, and regular discussions
about goals, performance, and challenges. This helps to build trust and
transparency within the organization.
3. Employee
Empowerment: In a democratic
leadership style, employees are given the autonomy and freedom to contribute
their ideas and make decisions related to their work. This empowerment leads to
increased motivation and a stronger sense of responsibility.
4. Collaboration and
Teamwork: Democratic leaders
emphasize collaboration and teamwork. They encourage employees to work
together, share knowledge, and support one another in achieving common goals.
This fosters a positive work environment and strengthens team cohesion.
5. Recognition and
Support: Democratic leaders
provide recognition and support for their employees’ contributions. By
acknowledging individual and team achievements, they motivate employees to
continue working toward shared objectives.
Advantages
of Democratic Leadership
1.
Increased
Employee Motivation and Engagement:
Because employees have a voice in decision-making, they are more likely to feel
valued and engaged in their work. This sense of involvement and responsibility
can lead to higher levels of motivation and commitment to the organization’s
goals.
2. Fostering
Creativity and Innovation: By
encouraging employees to share their ideas and opinions, democratic leaders
create an environment that fosters creativity and innovation. This open
exchange of ideas can lead to new solutions, improved processes, and greater
organizational adaptability.
3. Higher Job
Satisfaction: Employees who feel
that their contributions are respected and their voices are heard are likely to
experience greater job satisfaction. A democratic leadership style fosters a
positive work environment, which can contribute to higher employee retention
rates.
4. Improved
Problem-Solving: Democratic
leaders can benefit from the diverse perspectives and expertise of their team members.
By incorporating a variety of viewpoints, democratic leaders are more likely to
arrive at well-rounded and effective solutions to problems.
5. Stronger Team
Cohesion: As democratic leaders
promote collaboration and teamwork, employees are more likely to develop strong
working relationships with one another. This sense of camaraderie can enhance
team performance and create a supportive work environment.
Disadvantages
of Democratic Leadership
1.
Slow
Decision-Making: One of the main
disadvantages of democratic leadership is that decision-making can be slow.
Since the leader involves employees in the process, it may take longer to reach
a consensus, especially when there are differing opinions or complex issues to
address.
2. Potential for
Conflict: While democratic
leadership promotes open communication, it can also lead to conflicts or
disagreements when team members have differing views. The leader must navigate
these conflicts and ensure that the decision-making process remains productive
and focused on organizational goals.
3. Leaders May Lose
Control: In a highly
participative environment, democratic leaders may struggle to maintain control
over decision-making. If too many voices are included in the process, the
leader may find it difficult to maintain a clear vision or direction for the
team.
4. Lack of Clear
Direction: Because democratic
leadership emphasizes collaboration, there may be times when team members are
unsure about the final decision or the direction of the organization. This can
lead to confusion or ambiguity in achieving specific goals.
When is
Democratic Leadership Effective?
The democratic
leadership style is particularly effective in environments where creativity,
innovation, and employee satisfaction are prioritized. It works well in
industries such as technology, research and development, education, and
creative fields, where input from multiple team members can lead to valuable
insights and solutions. Additionally, democratic leadership is beneficial in
organizations that value employee development and strive to create a positive,
inclusive workplace culture. However, it may not be suitable for organizations
or situations that require quick decision-making or tight control, as the
collaborative nature of this style can lead to delays in reaching conclusions.
Comparison of Autocratic and Democratic Leadership Styles
Autocratic and
democratic leadership styles represent two ends of the leadership spectrum,
each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The autocratic style is characterized by centralized
decision-making, clear structure, and tight control, which can be effective in
crisis situations or environments that require efficiency and precision.
However, this style often leads to lower levels of employee motivation and
engagement, and it can stifle creativity and innovation.
In contrast, the democratic style is characterized by shared
decision-making, open communication, and employee empowerment. This style
fosters a collaborative work environment that can lead to higher levels of
employee satisfaction, motivation, and creativity. However, it may result in
slower decision-making processes and potential conflicts among team members.
The choice between autocratic and democratic
leadership depends largely on the context in which the leadership is being
applied. Autocratic leadership may be appropriate in situations that require
quick, decisive action or when employees need clear direction and structure. On
the other hand, democratic leadership is more effective in environments that
value collaboration, creativity, and employee involvement.
Conclusion
In conclusion,
both the autocratic and democratic leadership styles have
distinct advantages and disadvantages, and the effectiveness of each style
depends on the specific context and needs of the organization. Autocratic
leadership offers quick decision-making and clear direction but may result in
low employee motivation and creativity. Democratic leadership, on the other
hand, promotes collaboration, employee engagement, and innovation but may lead
to slower decision-making and potential conflict. Successful leaders often
adapt their leadership style to the demands of the situation, balancing the
need for control with the desire for employee involvement. Understanding the
strengths and limitations of these two leadership styles is essential for leaders
who wish to maximize their effectiveness and create a positive organizational
culture.









0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.