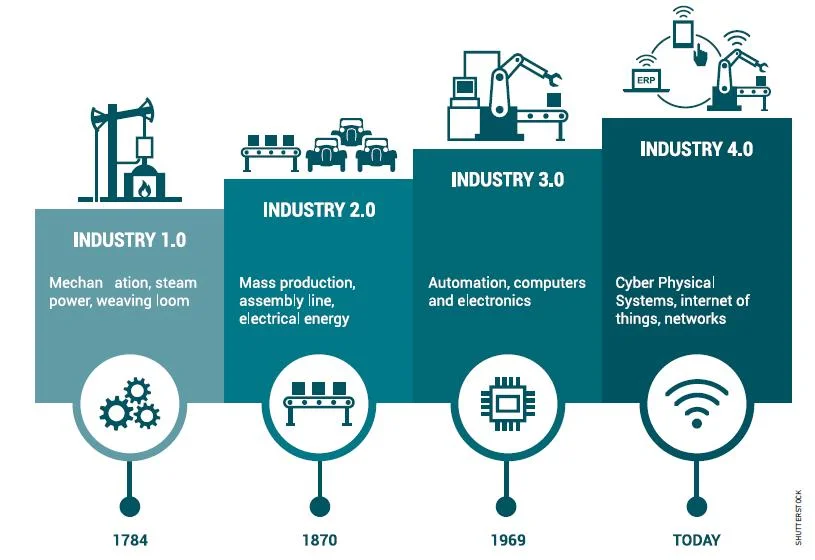
Q. What is Industry 4.0? Explain the evolution of Industry 4.0 and its applications in Business and society.
Sustainable Operations Management: A
Comprehensive Overview
In the contemporary business
landscape, the concept of sustainability has transcended mere ethical
considerations to become a critical driver of organizational success.
Sustainable operations management (SOM) has emerged as a vital discipline that
integrates economic, environmental, and social dimensions into the core of
operational strategies, processes, and practices. This comprehensive approach
aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of
future generations to meet their own needs.
SOM is underpinned by
several fundamental principles that guide organizations in their pursuit of
sustainable practices:
1. Triple Bottom Line (TBL)
Approach:
SOM embraces the TBL framework, which emphasizes the interconnectedness of
economic, environmental, and social performance. Organizations are expected to
consider the impact of their operations on all three dimensions, striving for a
balance that ensures long-term viability and value creation.
2. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): SOM incorporates LCA, a
methodology that evaluates the environmental impacts of
a product or service throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material
extraction
3. Resource
Efficiency: SOM prioritizes the efficient use of resources, including energy,
water, materials, and land. Organizations are encouraged to adopt strategies
such as waste reduction, recycling, and closed-loop systems to minimize
resource depletion and environmental degradation.
4. Stakeholder Engagement: SOM recognizes the
importance of engaging with stakeholders, including employees, customers,
suppliers, communities, and investors. Organizations are expected to consider
the interests and concerns of stakeholders in their decision-making processes,
fostering transparency and collaboration.
5. Ethical Considerations: SOM emphasizes ethical
conduct in all aspects of operations, including labor practices, human rights,
and fair trade. Organizations are expected to uphold ethical standards
throughout their supply chains, ensuring that their operations contribute to
social well-being.
6. Continuous Improvement: SOM promotes a culture of
continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to constantly seek ways to
enhance their sustainability performance. This involves setting ambitious
targets, monitoring progress, and adapting strategies to achieve optimal
outcomes.
Importance of Sustainability for Business
Sustainability has become a
strategic imperative for businesses due to several compelling reasons:
1. Enhanced Brand Reputation: Consumers are increasingly
conscious of environmental and social issues, favoring brands that demonstrate
a commitment to sustainability. Organizations with strong sustainability
credentials can enhance their brand reputation, attracting customers and
building loyalty.
2. Cost Savings: Sustainable practices often
lead to cost savings through resource efficiency, waste reduction, and energy
conservation. By minimizing environmental impacts, organizations can reduce
operational expenses and improve profitability.
3. Competitive Advantage: Sustainability can be a
source of competitive advantage, enabling organizations to differentiate
themselves from competitors and attract investors who prioritize environmental,
social, and governance (ESG) factors.
4. Risk Mitigation: Sustainability helps
organizations mitigate risks related to environmental regulations, resource
scarcity, and social conflicts. By proactively addressing these challenges,
businesses can ensure long-term resilience and stability.
5. Innovation Opportunities: Sustainability can drive
innovation, encouraging organizations to develop new products, services, and
processes that are environmentally and socially responsible. This can lead to
new market opportunities and revenue streams.
6. Talent Attraction and
Retention: Employees are increasingly drawn to organizations that align with
their values, including sustainability. Businesses with strong sustainability
practices can attract and retain top talent, fostering a motivated and engaged
workforce.
The Notion of Sustainability
The concept of
sustainability encompasses a broad range of environmental, social, and economic
considerations. It is often defined as "meeting the
needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to
meet their own needs." This
Sustainability
is not solely focused on environmental protection; it also encompasses social
and economic dimensions. The social dimension of sustainability addresses
issues such as human rights, labor standards, community development, and social
justice. The economic dimension focuses on creating a stable and prosperous
economy that provides opportunities for all, while respecting environmental
limits.
Challenges in Creating
Sustainable Operations
Organizations face numerous
challenges in their efforts to create sustainable operations:
1. Conflicting Priorities: Balancing economic,
environmental, and social objectives can be challenging, as these dimensions
may sometimes conflict. Organizations need to find ways to integrate
sustainability into their core business strategies, ensuring that it is not
treated as a separate initiative.
2. Measuring and Reporting
Performance: Measuring and reporting sustainability performance can be complex, as
it involves tracking a wide range of environmental, social, and economic
indicators. Organizations need to develop robust systems for data collection,
analysis, and reporting to effectively monitor their progress.
3. Supply Chain Complexity: Managing sustainability
across global supply chains can be challenging due to the involvement of
multiple suppliers, each with their own environmental and social practices.
Organizations need to extend their sustainability efforts to their supply chains,
ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical and environmental standards.
4. Lack of Awareness and
Understanding: Many organizations lack awareness and understanding of sustainability
principles and practices. This can hinder their ability to implement effective
sustainability initiatives. Organizations need to invest in training and
education to raise awareness and build capacity.
5. Resistance to Change: Implementing sustainable
operations often requires significant changes to existing processes and
practices. This can encounter resistance from employees who are comfortable
with the status quo. Organizations need to effectively communicate the benefits
of sustainability and engage employees in the change process.
6. Cost Considerations: Investing in sustainable technologies
and practices can be costly, which may deter some organizations from pursuing
sustainability initiatives. However, organizations need to recognize that
sustainability can also lead to cost savings in the long run through resource
efficiency and waste reduction.
Conclusion
Sustainable operations
management is an essential discipline for organizations seeking to thrive in
the 21st century. By integrating economic, environmental, and social dimensions
into their core operations, businesses can enhance their brand reputation,
reduce costs, gain a competitive advantage, and mitigate risks. While
challenges exist in creating sustainable operations, organizations that embrace
sustainability principles and practices will be better positioned to achieve long-term
success and contribute to a more sustainable future.







0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.