Q. How does a political environment within a country impact the business and operation of firms? Explain.
Introduction: The Political Environment and Business Operations
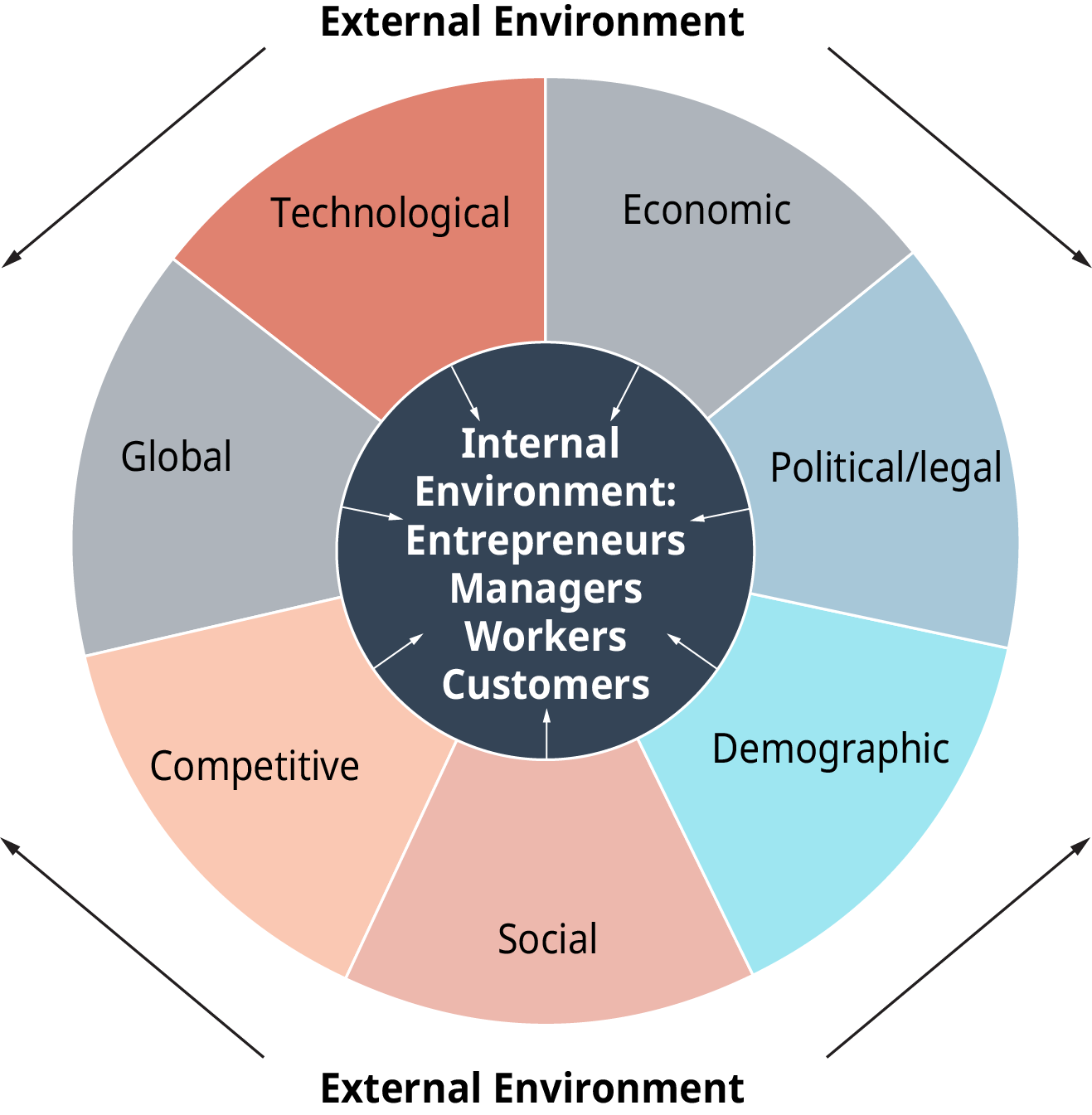
The political
environment refers to the political factors, structures, and processes
that affect businesses, industries, and markets. This environment encompasses
the policies, regulations, laws, political stability, governance structures,
and the general political climate in a given country. The political environment
plays a significant role in shaping the way businesses operate within a
country. The decisions made by governments, political parties, and elected
officials influence everything from tax policies and labor laws to foreign
investment policies and international trade agreements.
In this context,
understanding how political factors affect business operations is crucial for
managers, business owners, and investors alike. In this detailed discussion, we
will explore the various ways in which the political environment influences
business practices and strategies.
1. Government
Policies and Regulations
Government
policies, laws, and regulations are central components of the political
environment that directly impact business operations. These policies can either
create opportunities or impose constraints on businesses. Key areas where
government policies influence business include:
a. Taxation
Policies
Taxation policies
are one of the most significant aspects of government intervention in business
operations. Corporate tax rates, value-added tax (VAT), sales taxes, and income
taxes directly affect a firm's profitability and overall financial performance.
For example, high corporate tax rates can reduce a company’s after-tax profits,
whereas low taxes may incentivize companies to invest and expand operations.
- Example: In
countries with low corporate tax rates like Ireland, businesses are more
likely to establish headquarters or operational facilities, as the tax
savings provide a competitive advantage.
Conversely, tax
policies can also have negative effects. For instance, governments might
increase taxes during economic crises to generate revenue, which can reduce
consumer spending and corporate profits.
b. Labor
Laws
Labor laws set by
governments govern the relationship between employers and employees, defining
minimum wage requirements, working hours, health and safety regulations, and
employee benefits. These laws vary significantly across countries, and
businesses need to comply with them to avoid penalties and legal issues.
- Example: In some
countries, such as Germany, strict labor laws that emphasize worker
protection, high wages, and strong union involvement may increase labor
costs for firms. In contrast, more flexible labor laws in countries like
the United States might lower operational costs but may result in less job
security and higher employee turnover.
These labor laws
also impact the way firms manage their human resources, their staffing
strategies, and their operating costs. Companies may find it more difficult to
expand in countries with rigid labor laws or face greater operational costs due
to high compliance requirements.
c. Environmental
Regulations
Environmental
regulations are increasingly becoming a significant concern for businesses
operating globally. Governments impose rules and regulations to ensure that
companies comply with sustainability standards, reduce pollution, and engage in
responsible production practices. These policies can directly affect business
costs, operational methods, and product designs.
- Example: Firms in
the European Union must comply with stringent environmental laws related
to carbon emissions, waste management, and recycling. While this may
increase operational costs, it can also create opportunities for
businesses that offer green or sustainable products and services.
d. Trade
and Import-Export Policies
Government trade
policies, tariffs, import/export restrictions, and subsidies play a significant
role in shaping the business environment, particularly for companies engaged in
international trade. Trade policies influence the cost of raw materials, the price
of finished goods, and a company’s ability to expand into foreign markets.
- Example: If a
government imposes tariffs on imported goods, this could increase the cost
of raw materials for domestic manufacturers, thereby reducing their
profitability. On the other hand, free trade agreements can open up new
markets and reduce operational costs by facilitating easier access to
foreign resources.
Governments also
impact the ability of businesses to enter new markets. If a country adopts
protectionist trade policies, it may make it harder for foreign companies to
operate within that market, while liberal trade policies can encourage
international investment.
2. Political
Stability and Governance
The stability of
the political environment is one of the most important factors affecting
business operations. Political stability is a critical condition for businesses
as it ensures that firms can operate without the constant fear of policy
changes, upheaval, or unrest. Countries with stable political environments
provide an environment conducive to investment and long-term planning.
a. Investment
Climate
Countries with stable
political environments attract more foreign direct investment (FDI) because
investors seek predictability and low political risk. In contrast, political
instability (e.g., coups, revolutions, civil wars) can deter investment,
disrupt business operations, and lead to a loss of capital.
- Example: Many
multinational companies have hesitated to invest in countries experiencing
political turmoil, such as Venezuela, because the political instability
introduces significant risks to their operations.
The presence of a
strong, transparent, and efficient governance structure
ensures that laws and regulations are applied consistently, and corruption is
minimized. Businesses are more likely to thrive in a market where the
government is perceived as legitimate, efficient, and free from corruption.
b. Regime
Change and Policy Uncertainty
Political
transitions or regime changes can create uncertainty for businesses. When there
is a change in government or leadership, the new regime may introduce new
policies, regulations, or taxes that affect businesses.
- Example: In the
United States, the shift from one presidential administration to another
may result in changes to healthcare, taxation, or trade policies, which
can significantly impact businesses operating in those sectors.
This political
uncertainty may lead firms to delay investment decisions, reduce long-term
planning, or divert capital to safer regions or industries.
3. Corruption and Bureaucracy
Corruption and
bureaucracy can severely hamper business operations, especially in developing
countries or countries with weak political systems. Corruption can create
unfair competition, increase costs, and distort market operations, making it
difficult for businesses to thrive.
a. Bribery
and Unofficial Payments
In countries where
corruption is rampant, businesses may be forced to make illegal payments to
government officials in exchange for favorable treatment, licenses, permits, or
government contracts. This can create an uneven playing field and lead to
higher operational costs.
- Example: A company
in a highly corrupt country might have to pay bribes to local officials to
expedite permits or get access to essential resources, thus inflating
their operating costs.
Such practices can
also damage a company’s reputation, undermine trust with customers and
stakeholders, and expose it to legal risks.
b. Bureaucratic
Processes and Red Tape
In some countries,
excessive bureaucracy and cumbersome regulatory processes can make it difficult
for businesses to operate efficiently. Long delays in getting approvals,
permits, and licenses can slow down business expansion, increase costs, and
reduce overall productivity.
- Example: In many
developing countries, the process of starting a business or obtaining permits
may be slow, requiring firms to navigate through layers of red tape. This
can delay time-to-market and increase the cost of doing business.
Reducing
corruption and improving government efficiency can significantly enhance the
business climate, making it easier for firms to operate and invest.
4. Political Ideology and Business Environment
The political
ideology of a country’s government can also significantly impact the business
environment. Governments with socialist, capitalist, or mixed-market economies
can introduce policies that shape the types of businesses that thrive and how
they operate.
a. Socialist Governments
In countries with
socialist governments, businesses may face higher levels of government control,
regulation, and intervention. State ownership of key industries, price
controls, and labor rights may limit the freedom of businesses to operate as
they see fit.
- Example: In
socialist or communist countries like Cuba or North Korea, businesses are
heavily regulated, and many industries are state-owned. Private businesses
may find it difficult to operate or expand.
b. Capitalist Governments
In capitalist
economies, businesses often operate with less government intervention, leading
to greater freedom in terms of pricing, competition, and innovation. The focus
in these economies is on market-driven forces, and companies are incentivized
to be competitive and efficient.
- Example: In
countries like the United States, businesses enjoy a high degree of
freedom to compete in the market, set prices, and innovate. However, this
may come with less government support in the form of subsidies or
regulations compared to socialist economies.
c. Mixed-Market Economies
Many countries
adopt a mixed-market approach, where the government plays a regulatory role but
businesses are primarily driven by market forces. In these economies, the
government might intervene to regulate certain industries while allowing others
to operate freely.
- Example: Countries
like India and China follow a mixed-market approach where the government
regulates certain sectors (e.g., banking, energy), while private
businesses thrive in other sectors like technology and consumer goods.
The political
ideology thus directly influences the level of government control, industry
protection, and freedom in the business environment.
5. International Relations and Geopolitical
Factors
A country’s
political environment also extends to its foreign policy and international
relations, which can have significant effects on businesses that
operate internationally. Diplomatic relations, trade agreements, and geopolitical
tensions all play a role in determining how firms interact with foreign markets
and governments.
a. Trade Agreements and Diplomatic Relations
Countries that
maintain favorable trade relationships, such as through free trade
agreements (FTAs), can create more opportunities for businesses. These
agreements can reduce tariffs, remove trade barriers, and make it easier for
firms to enter new markets.
- Example: The North
American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now replaced by the United
States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), facilitated trade between the
three countries by reducing tariffs and simplifying trade processes.
On the other hand,
political tensions or trade wars between countries can disrupt supply chains,
increase tariffs, and create barriers to market access, affecting international
businesses.
b. Geopolitical Instability
Geopolitical
instability, such as wars, terrorism, or conflicts, can create significant
risks for businesses operating in affected regions. Political unrest or civil
wars can lead to the disruption of supply chains, increased insurance costs, or
even the loss of assets.
- Example:
Businesses in the Middle East or North Africa have to account for the
political risks of instability, which can affect their ability to operate
smoothly or safely in certain countries.
Conclusion
The political
environment plays a central role in shaping the way businesses operate
and make strategic decisions. Government policies, political stability,
regulatory frameworks, corruption levels, and geopolitical dynamics all impact
a firm’s ability to succeed or fail. A stable, transparent, and supportive
political environment can foster business growth, while instability, high
corruption, and unfavorable policies can create significant challenges.
Businesses must
carefully monitor political changes, engage in strategic planning, and manage
risks associated with political uncertainty to thrive in a dynamic global
market. Whether through favorable tax policies, labor laws, or international
trade relations, the political environment is an essential factor for any
business looking to expand, invest, or operate effectively in a given country.
Understanding these political dynamics is critical for firms to develop
adaptive strategies, manage risk, and ultimately achieve success in the global
economy.







0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.