Q. Discuss the relevance of ‘Risk Management’. What are the steps involved in the Risk Management process?
Risk
management is a critical process for any organization, regardless of size or
industry. It's not merely about avoiding negative outcomes; it's about
proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to achieve
objectives, protect resources, and enhance overall performance. In essence,
risk management is about making informed decisions in the face of uncertainty. Its
relevance spans every facet of an organization, from strategic planning and
financial management to operational efficiency and project execution. Without a
robust risk management framework, organizations are vulnerable to unforeseen
events that can disrupt operations, damage reputation, and even threaten their
survival.
The
modern business environment is characterized by increasing complexity,
volatility, and interconnectedness. Globalization, technological advancements,
evolving regulatory landscapes, and geopolitical uncertainties all contribute
to a heightened level of risk. In this dynamic context, effective risk
management is no longer a luxury but a necessity for sustainable success.
Here's a deeper look at its relevance:
- Strategic Decision-Making: Risk management provides a structured approach to
evaluating the potential impact of various strategic options. By
identifying and assessing the risks associated with different strategies,
organizations can make more informed choices that align with their overall
goals and risk appetite. It helps to prioritize initiatives, allocate
resources effectively, and develop contingency plans.
- Protecting Assets and
Resources: Organizations invest
significant resources in physical assets, intellectual property, human
capital, and financial resources. Risk management helps to safeguard these
assets by identifying potential threats such as natural disasters,
cyberattacks, fraud, and operational disruptions. By implementing
appropriate controls and mitigation strategies, organizations can minimize
losses and ensure business continuity.
- Enhancing Operational
Efficiency: Risks can significantly impact
operational efficiency by causing delays, errors, and cost overruns. Risk
management helps to identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and
implement quality control measures to minimize operational disruptions and
improve productivity. It fosters a proactive approach to problem-solving
and continuous improvement.
- Improving Project Outcomes: Projects are inherently risky due to uncertainties
related to scope, budget, timeline, and resources. Risk management is
essential for successful project execution. It enables project managers to
identify potential roadblocks, develop mitigation plans, and proactively
manage risks throughout the project lifecycle. This increases the
likelihood of delivering projects on time, within budget, and to the
required quality standards.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Unexpected events such as natural disasters,
pandemics, or supply chain disruptions can severely impact business
operations. Risk management plays a vital role in ensuring business
continuity by developing disaster recovery plans, establishing backup
systems, and implementing crisis communication protocols. This allows
organizations to quickly recover from disruptions and minimize downtime.
- Protecting Reputation and Brand
Value: Negative events such as
product recalls, data breaches, or ethical lapses can severely damage an
organization's reputation and brand value. Risk management helps to
identify and mitigate reputational risks by implementing ethical
guidelines, ensuring product safety, and protecting customer data. It
fosters a culture of transparency and accountability.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to various regulations
related to safety, environmental protection, data privacy, and financial
reporting. Risk management helps organizations to identify and comply with
these regulations, avoiding penalties and legal liabilities. It ensures
that the organization operates within the legal and ethical framework.
- Improving Stakeholder
Confidence: Investors, customers,
employees, and other stakeholders are increasingly concerned about risk
management practices. Organizations with robust risk management frameworks
are viewed as more stable, reliable, and trustworthy. This enhances
stakeholder confidence and can lead to improved access to capital,
stronger customer relationships, and increased employee engagement.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that effectively manage risks are better positioned to seize opportunities and adapt to changing market conditions. They are more agile, resilient, and innovative. This can provide a significant competitive advantage in the marketplace.
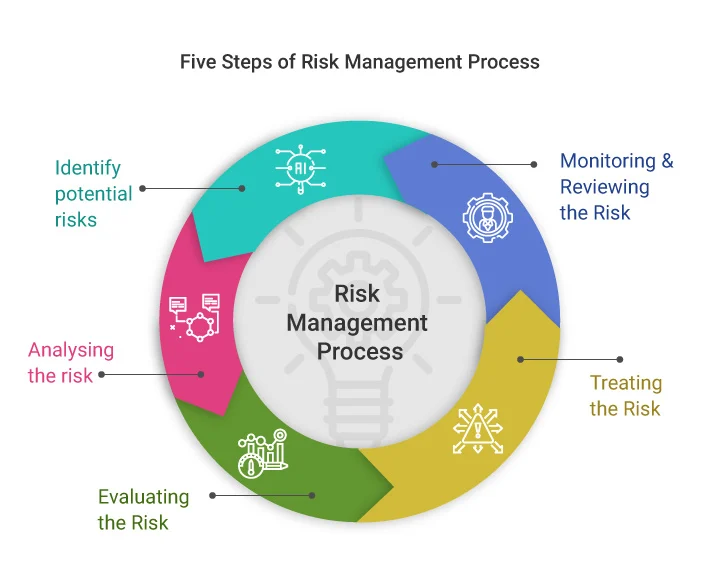
Steps Involved in the Risk Management Process:
The
risk management process is a systematic and iterative cycle that involves
several key steps:
1.
Risk
Identification: This is the crucial first step
where potential risks are identified and documented. It involves brainstorming,
conducting surveys, analyzing historical data, and consulting with experts to
identify anything that could potentially impact the organization's objectives.
Risks can be categorized in various ways, such as strategic, operational,
financial, compliance, reputational, and technological. It's important to
consider both internal and external risks. Techniques like SWOT analysis,
PESTLE analysis, and risk registers can be helpful in this stage.
2.
Risk
Analysis: Once risks are identified, they
need to be analyzed to understand their potential impact and likelihood of
occurrence. This involves assessing the severity of the consequences and the
probability of the risk event happening. Qualitative methods, such as risk
matrices, can be used to categorize risks based on their impact and likelihood.
Quantitative methods, such as Monte Carlo simulations, can provide more precise
estimates of risk exposure.
3.
Risk
Evaluation/Assessment: This step
involves prioritizing risks based on their level of significance. Risks with
the highest potential impact and likelihood are given the highest priority.
This helps organizations to focus their resources on managing the most critical
risks. Risk appetite, which is the level of risk an organization is willing to
accept, plays a crucial role in risk evaluation.
4.
Risk
Response/Mitigation: Once risks are evaluated,
appropriate risk responses need to be developed and implemented. There are
several common risk response strategies:
o Avoidance:
This involves eliminating the risk altogether by ceasing the activity or
project that gives rise to the risk.
o Reduction:
This involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This
can be achieved through implementing controls, improving processes, or
diversifying resources.
o Transfer:
This involves shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or
outsourcing.
o Acceptance:
This involves acknowledging the risk and making a conscious decision to accept
it without taking any action. This may be appropriate for low-impact,
low-likelihood risks.
5.
Risk
Monitoring and Review: Risk
management is an ongoing process. Risks need to be continuously monitored and
reviewed to ensure that the risk responses are effective and that new risks are
identified. This involves tracking risk indicators, conducting regular risk
assessments, and updating the risk management plan as needed. Regular reporting
on risk management activities is also essential.
6.
Communication
and Consultation: Effective communication and consultation
with stakeholders are crucial throughout the risk management process. This
ensures that everyone is aware of the risks and the risk management strategies
that are being implemented. Stakeholder input can also be valuable in
identifying and assessing risks.
7.
Documentation
and Reporting: Maintaining proper documentation of
the risk management process is essential for accountability and continuous
improvement. This includes documenting the identified risks, the risk analysis,
the risk responses, and the monitoring activities. Regular reporting on risk
management activities to senior management and other stakeholders is also
important.
Integrating
Risk Management:
For
risk management to be truly effective, it needs to be integrated into the
organization's culture and decision-making processes. This requires strong
leadership support, clear communication, and training for all employees. Risk
awareness should be embedded in all aspects of the organization's operations,
from strategic planning to day-to-day activities.
Continuous
Improvement:
The
risk management process should be continuously reviewed and improved. Lessons
learned from past risk events should be captured and used to update the risk
management framework. Organizations should also stay abreast of emerging risks
and adapt their risk management strategies accordingly.
In
conclusion, risk management is an essential process for any organization
seeking to achieve its objectives, protect its resources, and thrive in an
increasingly complex and uncertain world. By implementing a robust risk
management framework, organizations can make informed decisions, minimize
losses, enhance operational efficiency, and build stakeholder confidence. It's
not about eliminating all risks, which is often impossible, but about
understanding and managing them effectively to maximize opportunities and
achieve sustainable success.







0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.