Explain the human-environment relationship by taking examples of biotic and abiotic components
The human-environment relationship refers to the interactions
between human societies and the natural world. This relationship is complex and
multi-faceted, and it involves both biotic and abiotic components of the
environment.
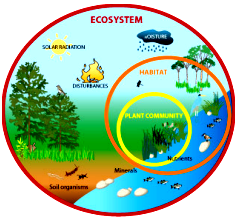
- Biotic components: Biotic components of the environment include living organisms such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. An example of the human-environment relationship involving biotic components is agriculture. Humans have been cultivating crops for thousands of years, and this activity has had a significant impact on the environment. Agriculture can lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and soil erosion. However, it can also be managed in a sustainable way that preserves biodiversity and ecosystems, while providing food and other resources for human populations.
- Abiotic components: Abiotic components of the environment include non-living elements such as water, air, and soil. An example of the human-environment relationship involving abiotic components is pollution. Human activities such as industrialization, transportation, and urbanization have led to the release of pollutants into the air, water, and soil. These pollutants can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, such as acid rain, air pollution and soil contamination, but measures can be taken to reduce the pollution and manage it sustainably.
In summary, the human-environment relationship is complex and
multifaceted, and it involves both biotic and abiotic components of the
environment. Humans have had a significant impact on the environment and
continue to do so. It is important for humans to understand this relationship
and take steps to manage it in a sustainable way that preserves the environment
for future generations.
What is the relationship between biotic and abiotic elements in the
environment
The relationship between biotic and abiotic elements in the
environment is one of interdependence. Biotic elements, such as plants and
animals, depend on abiotic elements, such as water, air, and soil, for
survival. At the same time, abiotic elements are also affected by biotic
elements.
- Biotic elements depend on abiotic elements: Living organisms, such as plants and animals, require certain abiotic elements in order to survive. For example, plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to carry out photosynthesis, and animals need air and water to breathe and survive.
- Abiotic elements are affected by biotic elements: Biotic elements, such as plants and animals, can also affect the abiotic elements of the environment. For example, plants release oxygen into the air through the process of photosynthesis and animals release carbon dioxide through respiration. This process is part of the carbon cycle, which regulates the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
- Mutual dependency and feedback loop: The relationship between biotic and abiotic elements is a mutual dependency and feedback loop. Changes in one element will affect the other, creating a balance in the ecosystem. This balance is important for the survival of all living organisms in the ecosystem.
- Interactions between biotic and abiotic components: The interactions between biotic and abiotic elements in the environment are complex and can occur on many different levels, from individual organisms to entire ecosystems. These interactions can be both positive and negative. For example, a plant may use a nutrient from the soil and in return, it may add organic matter that enriches the soil. On the other hand, pollution may have negative effects on both biotic and abiotic elements.
Overall, biotic and abiotic elements in the environment are
interconnected and dependent on each other. The balance between these elements
is essential for the survival of living organisms and the maintenance of
ecosystem functions.
Can you describe the relationship and interaction between biotic and
abiotic components
The relationship and interaction between biotic and abiotic
components in the environment is complex and multifaceted. Biotic components
include all living organisms such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, while
abiotic components include non-living elements such as water, air, soil,
temperature, and light.
- Biotic components depend on abiotic components: Bioticcomponents, such as plants and animals, depend on abiotic components for survival. For example, plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to carry out photosynthesis, while animals need air and water to breathe and survive.
- Abiotic components are affected by biotic components: Biotic components can also affect the abiotic components of the environment. For example, plants release oxygen into the air through the process of photosynthesis and animals release carbon dioxide through respiration. This process is part of the carbon cycle, which regulates the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
- Mutual dependency and feedback loop: The relationship between biotic and abiotic components is a mutual dependency and feedback loop. Changes in one component will affect the other, creating a balance in the ecosystem. This balance is important for the survival of all living organisms in the ecosystem.
- Interactions between biotic and abiotic components: The interactions between biotic and abiotic components in the environment can occur on many different levels, from individual organisms to entire ecosystems. For example, in a food web, one organism may be a predator and another may be its prey. This creates a complex web of interactions that affects the population of the different species and the ecosystem as a whole.
- Interactions can also be mutualistic or parasitic: The interactions between biotic and abiotic components can also be mutualistic, where both parties benefit, or parasitic, where one organism benefits at the expense of another. For instance, certain species of birds and insects are pollinators for plants, which benefits both the plants and the pollinators, or certain species of fungi live in mutualistic relationships with plants by providing them with nutrients in exchange for sugars.
Overall, the relationship and interaction between biotic and
abiotic components in the environment is complex and dynamic, with the balance
between these components being essential for the survival of living organisms
and the maintenance of ecosystem functions.
What is the abiotic and biotic elements that surround human
Humans are surrounded by both abiotic and biotic elements in
the environment.
Abiotic elements: Some of the abiotic elements that surround
humans include:
- Air: Humans require clean air to breathe, and they are constantly exposed to various forms of air pollution such as smog, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases.
- Water: Humans require water for drinking, bathing, and other daily activities. They also may be exposed to various forms of water pollution such as chemical and biological contaminants.
- Soil: Humans are in contact with soil through activities such as gardening, farming, and construction. Soil can be contaminated by various pollutants, such as pesticides and heavy metals, which can have negative effects on human health.
Temperature and light: Humans are affected by the temperature
and light of their environment, which can have an impact on their physical and
mental well-being.
Biotic elements: Some of the biotic elements that surround
humans include:
- Plants: Humans are surrounded by plants in the form of trees, grass, and other vegetation. They provide numerous benefits such as oxygen, food, and aesthetic value.
- Animals: Humans are surrounded by animals in the form of pets, livestock, and wild animals. They can provide companionship, food, and other benefits, but can also pose a threat to human health and safety.
- Microorganisms: Humans are constantly exposed to microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Some of these microorganisms can be beneficial, while others can cause illness.
Overall, humans are surrounded by a complex and dynamic
environment that includes both abiotic and biotic elements. Understanding the
interactions between these elements and their impact on human health is
important for making informed decisions about how to manage and protect the
environment.
What is an example of a biotic abiotic relationship
An example of a biotic-abiotic relationship is the symbiotic
relationship between plants and mycorrhizal fungi.
Mycorrhizal fungi form a mutualistic relationship with the
roots of most plants, where the fungi colonize the plant's roots and provide
the plant with nutrients, such as phosphorous, which the plant can't absorb
from the soil by itself. In return, the plant provides the fungi with sugars
through photosynthesis. This relationship helps the plants to grow better and
thrive in nutrient-poor soils and it also improves the soil structure, water
retention and increases the resistance to pathogens and pests.
This is one example of many biotic-abiotic relationships that
exist in an ecosystem and shows how living organisms rely on non-living
components of the environment, and how changes in the abiotic components can
have an impact on the biotic components. This is important to understand in
order to manage ecosystems in a sustainable way that preserves and enhances the
biodiversity and ecological services that benefit both the living and
non-living components of the environment.
For PDF , Handwritten
WhatsApp – 8130208920
(Send
Your Subject Code or Question paper)







0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.